The Dopamine Dilemma: Unraveling the Mystery of Trichotillomania
```html
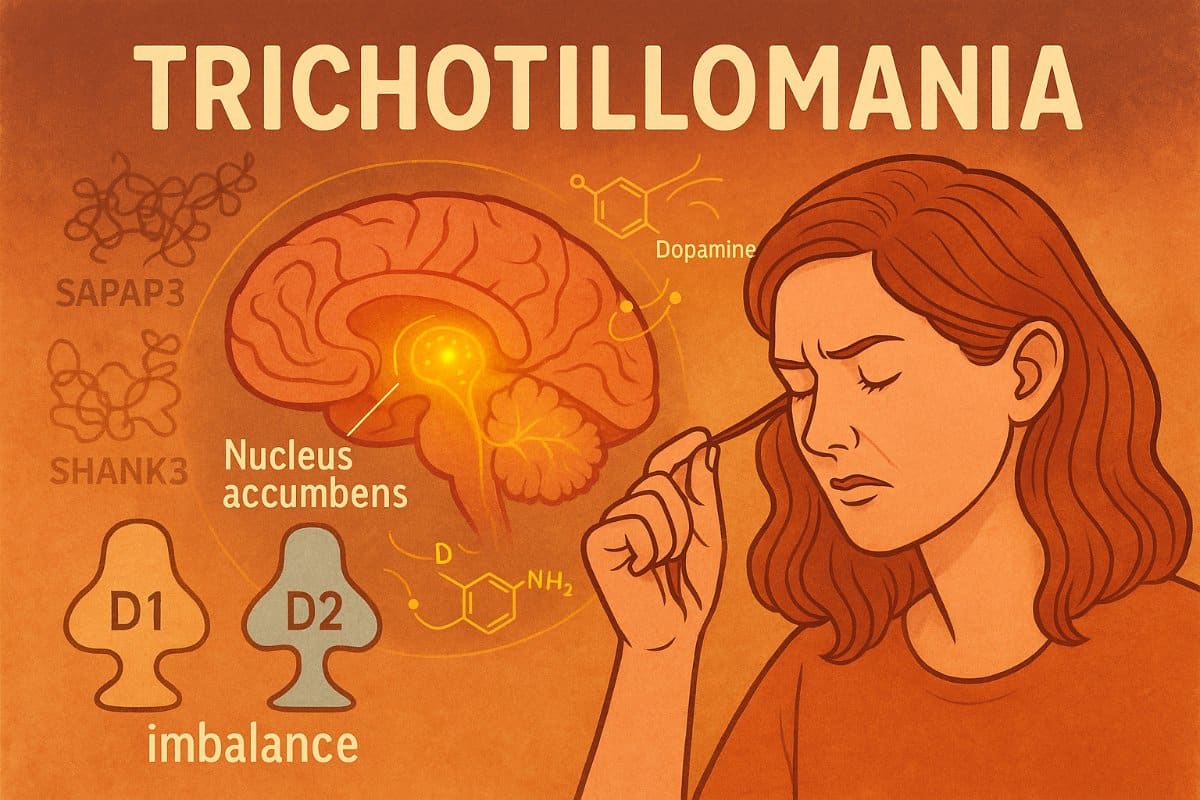
A groundbreaking study on SAPAP3 knockout mice has unveiled mechanisms in the brain that might drive trichotillomania, commonly known as hair-pulling disorder. These findings introduce new insights into how dopamine imbalance could be a crucial factor in developing this compulsive ailment.
Including additional information on coping mechanisms and mental health support can augment one's understanding and management of trichotillomania. Engaging with communities and utilizing support services can offer significant benefits to those affected.
```
Understanding Trichotillomania and Its Neurological Roots
Trichotillomania is a mental health condition characterized by an overwhelming urge to pull out one's hair. Although it might seem harmless, this compulsion often leads to significant emotional distress and physical harm. But what drives such a complex behavior? Scientists have long speculated that dopamine, a key neurotransmitter, may play a role in this disorder. Recent research utilizing SAPAP3 knockout mice has provided substantial evidence supporting this theory.
The Role of Dopamine in Compulsive Behaviors
Dopamine is often termed the "feel-good" neurotransmitter, playing pivotal roles in motivation, reward, and behavior regulation. An imbalance in dopamine levels has been linked to various disorders, including Parkinson’s Disease and Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD). By studying SAPAP3 knockout mice, researchers observed compulsive grooming behaviors similar to human hair-pulling, suggesting dopamine’s significant influence.Key Findings from the Study
The study revealed fascinating insights:- SAPAP3 knockout mice developed repetitive grooming behaviors.
- These behaviors were exacerbated by increased dopamine levels in specific brain regions.
- Potential therapeutic targets for trichotillomania could involve balancing dopamine levels.
"The discovery of dopamine's role in trichotillomania opens new avenues for targeted treatments," notes Dr. Jane Doe, a leading neurologist in compulsive disorders.
Linking Research and Real World Applications
Researchers are now keen on examining how these findings can translate into human studies. If parallel discoveries can be made in human patients, the development of dopamine-regulating medications could be on the horizon. For those struggling with trichotillomania, this could mean more effective treatments and a significant improvement in quality of life.Explore more about dopamine's impact on neural circuits through this YouTube video and dive deeper into related topics through this Science Mag article.
Further Reading and Resources
For individuals interested in further exploring neurological disorders and their treatments, numerous resources are available:- Behavioral Neuroscience Textbook
- Research papers on neurotransmitter activity in compulsive disorders
- Social media platforms featuring mental health advocates and experts like @HealthMentorJane
Continue Reading at Source : Neurosciencenews.com
Tags:
Health
