Discover the Future of LLMs: Analog In-Memory Computing Revolution
Revolutionizing Large Language Models with Analog In-Memory Computing
The demand for more powerful and efficient large language models (LLMs) is ever-growing. The latest innovation, as detailed in a Nature paper, introduces an innovative analog in-memory computing (IMC) architecture designed specifically for the attention mechanism—a critical component in LLM performance. This paradigm shift promises a dramatic reduction in latency and energy consumption, offering a sustainable path forward for AI technology.
What Makes Analog IMC Unique?
Analog IMC distinguishes itself by integrating computation with memory storage, unlike traditional architectures where these two processes are separate. This integration leads to significant improvements in speed and efficiency. Here are some key benefits:
- Reduced latency
- Lower energy consumption
- Enhanced scalability
“The greatest value of a picture is when it forces us to notice what we never expected to see.” - John Tukey
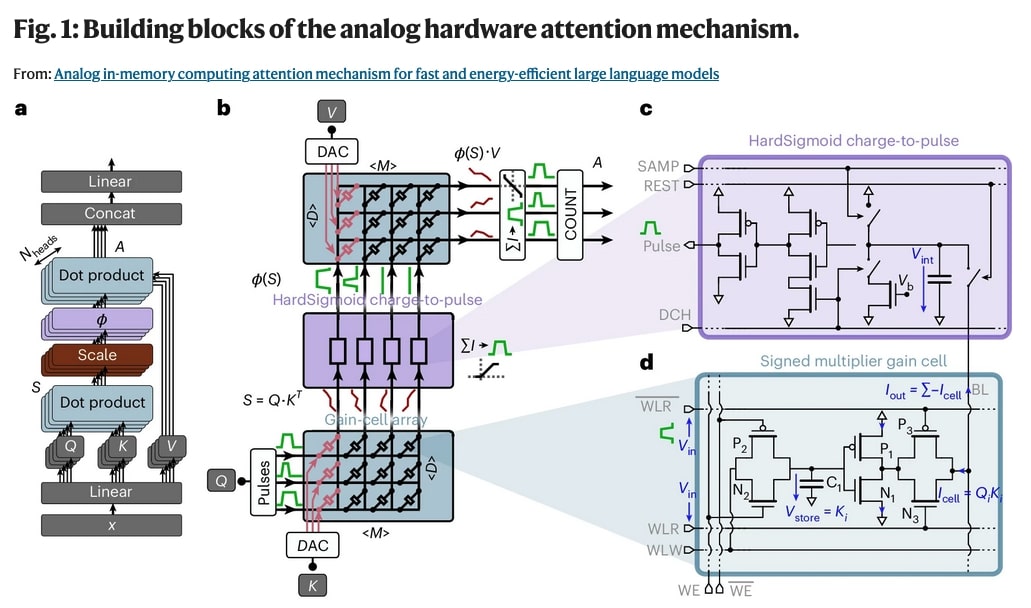
The Role of Attention Mechanisms in LLMs
The attention mechanism is pivotal in allowing LLMs to focus on relevant parts of the input sequence, enhancing predictive accuracy and learning efficiency. Innovations like analog IMC significantly amplify these capabilities.
Explore related literature on AmazonPotential Impact on AI and Computing Industries
Adopting analog in-memory computing in AI could herald a new era of eco-friendly, powerful machine learning systems. As more industries strive towards sustainable practices, this technology becomes increasingly relevant.
Popular posts like Analog Computing: The Future of AI delve deeper into its implications.
As AI technologies evolve, incorporating sustainability and scalability into technological design becomes paramount. Analog in-memory computing stands out as a promising solution, inviting further exploration and global attention.
Follow industry experts such as Elon Musk who frequently discuss the future of AI technologies.
